
Traces of An Ancient Human Culture From 40,000 Years Ago Unearthed In China
But who were they?
By Nicoletta Lanese | Live Science
Scientists discovered remnants of an Old Stone Age culture, less than 100 miles (160 kilometres) west of Beijing, where ancient hominins used a reddish pigment called ochre and crafted tiny, blade-like tools from stone.
The archaeological site, called Xiamabei, offers a rare glimpse into the life of Homo sapiens and now-extinct human relatives who inhabited the region some 40,000 years ago.
The newly excavated site lies within the Nihewan Basin, a depression in a mountainous region of northern China. The excavation team found evidence of the culture about 8 feet (2.5 meters) underground, when they spotted a layer of dark, silty sediment that dated to between 41,000 and 39,000 years ago, based on radiocarbon dating and other analyses.
This Stone Age sediment contained a treasure trove of artefacts and animal remains, including more than 430 mammal bones; a hearth; physical evidence of ochre use and processing; a tool made of bone; and more than 380 miniaturized lithics, or small tools and artefacts made of chipped or ground stone.
“The remains seemed to be in their original spots after the site was abandoned by the residents,” co-first author Shixia Yang, a researcher with the Chinese Academy of Sciences and the Max Planck Institute for the Science of Human History, told Live Science in an email.
“Based on this, we can reveal a vivid picture of how people lived 40,000 years ago in Eastern Asia.”
Identifying a 40,000-year-old sediment layer strewn with such artefacts was “a surprise,” co-senior author Francesco d’Errico, a CNRS Director of Research at the Bordeaux University and professor at the University of Bergen, told Live Science in an email.
Notably, “this is the earliest-known ochre workshop for East Asia“, and the collection of tiny stone tools suggests that the makers likely produced and used specialized tool kits, he said.
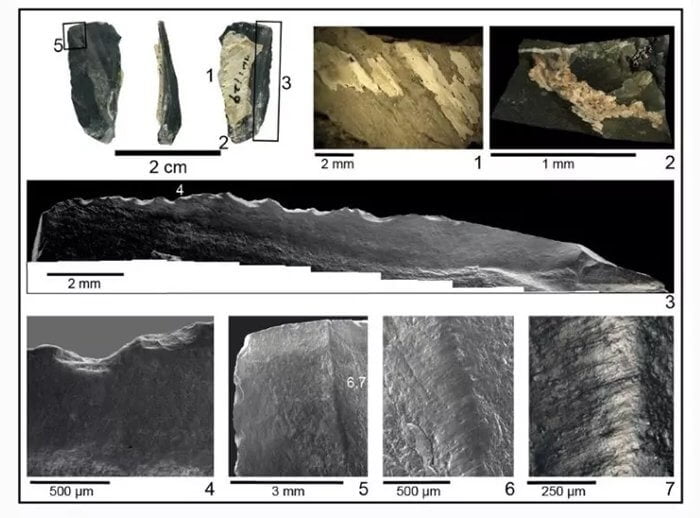
Above: Bladelet-like stones found at Xiamabei bear microscopic evidence of having been attached to a bone handle with plant fibres.
Yang, d’Errico, and their colleagues published a report about the site and artefacts on Wednesday (March 2) in the journal .
The evidence of ochre processing at Xiamabei includes two pieces of ochre with slightly different mineral compositions, as well as an elongated limestone slab with smoothed areas stained with the crimson pigment. The team found these artefacts in close proximity to one another, laying atop an area of reddened sediment.
“I do not think that anyone should find it shocking that the inhabitants of what is now northern China [40,000 years ago] were collecting and using ochre,” as, in general, humans and their relatives had been using the pigment for many years at that point, said Andrew M. Zipkin, an adjunct professor in the School of Human Evolution and Social Change at Arizona State University and an associate scientist at Eurofins EAG Laboratories, who was not involved in the study.
“The ochre artefacts in this study are pretty limited in number, but I would be excited [to] see follow-up work on them that seeks to identify where the ochre was collected,” Zipkin told Live Science in an email.
Regarding the new study, “for me, the important bit here is not the ochre in its own right, but its presence as part of a suite of technologies and behaviours,” he said.
The first ochre piece found at the site bore signs of having been “repeatedly abraded to produce a bright dark red ochre powder,” the authors reported; the second, smaller piece of ochre had a more crumbly texture, by comparison, and likely originated from a larger ochre piece that had been crushed.
An analysis led by d’Errico revealed that the different types of ochre had been pounded and scraped into powders of varying consistency.
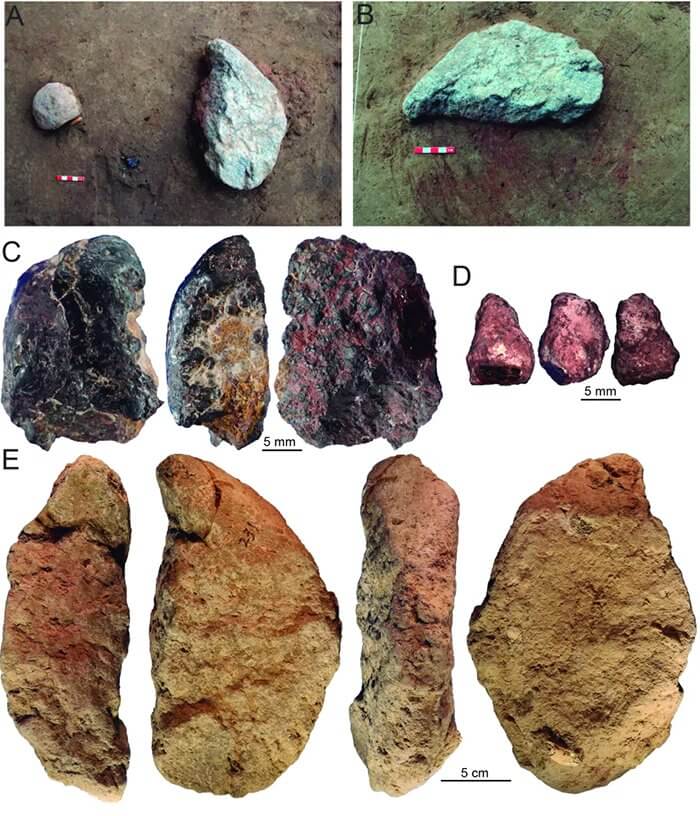
Above: Ochre pieces and processing equipment found at the site were discovered on a red-stained patch of sediment.
Another analysis showed that the reddish sediment found near the ochre contained rocky fragments rich in hematite, a mineral that contains oxidized iron and gives red ochre its distinct hue.
(Other types of ochre, including yellow ochre and so-called specularite, a sparkly, reddish-purple pigment, have slightly different mineral compositions, according to Discover.)
Based on the available evidence, however, they could not determine exactly how the pigment was used. Ochre can be used in adhesives, for example, or in “symbolic applications” such as rock art paint or paint that’s applied to the body as both cosmetic decoration and sunscreen, Zipkin said.
“Distinguishing between symbolic and functional uses of ochre in the material culture record is an on-going challenge for prehistoric archaeologists,” he noted.
Traces of ochre did crop up on several stone tools at the site, and the nature of these tools hinted that the pigment may have been used as an additive used in hide processing and as an ingredient in a hafting adhesive – meaning a sticky substance used to affix handles to stone tools.
This evidence does not negate the possibility that the pigment may have also been used symbolically, Zipkin said.
Archaeologists have uncovered evidence of ochre processing in Africa and Europe, to a lesser extent, dating back to about 300,000 years ago, and there’s evidence of ochre use in Australia starting about 50,000 years ago, d’Errico told Live Science.
But prior to the excavation of Xiamabei, “the evidence for ochre use in Asia before [28,000 years ago] was, however, very scant,” he said.
Based on patterns of wear and lingering residues on hafted lithics found at the site, the team determined that these artefacts were likely used for multiple purposes, including boring through materials, hide scraping, whittling plant material and cutting soft animal matter.
Likewise, the unhafted lithics were likely for several purposes, such as boring hard materials and cutting softer materials.
“We are therefore facing a complex technical system exploiting different raw materials to create highly effective, portable tools, used in a variety of activities,” d’Errico said.
Small stone blades known as microblades, or bladelets, became widely used in northeastern Asia by the end of the Pleistocene era (2.6 million to 11,700 years ago), Yang said; specifically, the technology began to spread throughout the region about 29,000 years ago, the authors noted in their report.
The lithics at Xiambei are not microblades but show similar features to the small stone tools, which lead Yang to wonder whether these objects represent the “root” of later microblade technology, she said.
The study raises another big question: Which archaic hominins actually occupied Xiamabei 40,000 years ago? Some clues point to modern humans, but the authors cannot be sure that human relatives – namely Neanderthals and Denisovans – weren’t present at the site.
“We cannot be certain that Homo sapiens occupied Xiamabei, owing to the lack of human fossils on site,” Yang told Live Science.
That said, modern human fossils have been found at a younger site called Tianyuandong, which lies about 68 miles (110 km) away, as well as another site in the region called the Zhoukoudian Upper Cave, she said. These nearby fossils hint that the ochre-processing, tool-crafting hominins that visited Xiamabei may have also been H. sapiens.
“We cannot, however, entirely disregard the possibility that other closely-related human ancestors were not still present in the vast landscapes of northern Asia, as it’s clear that earlier groups of Homo sapiens were mating and mixing with Neanderthals and Denisovans,” Yang said.
In addition, since Neanderthals also used ochre, the evidence of ochre use doesn’t offer any clues as to which hominins were present at the site, Zipkin said.
“Further planned excavations at Xiamabei will help us to better understand our evolutionary story,” Yang said.
This article was originally published by Live Science.
